Papers on drone navigation
The are my publications in relation to drone navigation in underground mines
- Autonomous MAV navigation in underground mines using darkness contours detectionIn International conference on computer vision systems 2019
This article considers a low-cost and light weight platform for the task of autonomous flying for inspection in underground mine tunnels. The main contribution of this paper is integrating simple, effi- cient and well-established methods in the computer vision community in a state of the art vision-based system for Micro Aerial Vehicle (MAV) navigation in dark tunnels. These methods include Otsu’s threshold and Moore-Neighborhood object tracing. The vision system can detect the position of low-illuminated tunnels in image frame by exploiting the in- herent darkness in the longitudinal direction. In the sequel, it is converted from the pixel coordinates to the heading rate command of the MAV for adjusting the heading towards the center of the tunnel. The efficacy of the proposed framework has been evaluated in multiple experimental field trials in an underground mine in Sweden, thus demonstrating the capability of low-cost and resource-constrained aerial vehicles to fly au- tonomously through tunnel confined spaces
@inproceedings{mansouri2019autonomous, title = {Autonomous {MAV} navigation in underground mines using darkness contours detection}, author = {Mansouri, Sina Sharif and Casta{\~n}o Arranz, Miguel and Kanellakis, Christoforos and Nikolakopoulos, George}, booktitle = {International conference on computer vision systems}, pages = {164--174}, year = {2019}, organization = {Springer, Cham}, }
-
 Where to look: a collection of methods for MAV heading correction in underground tunnelsIET Image Processing 2020
Where to look: a collection of methods for MAV heading correction in underground tunnelsIET Image Processing 2020Degraded Subterranean environments are an attractive case for miniature aerial vehicles, since there is a constant need to increase the safety operations in underground mines. The starting point for integrating aerial vehicles in the mining process is the capability to reliably navigate along tunnels. Inspired by recent advancements, this paper presents a collection of different, experimentally verified, methods tackling the problem of MAVs heading regulation while navigating in dark and textureless tunnel areas. More specifically, four different methods are presented in this work with the common goal to identify open space in the tunnel and align the MAV heading using either visual sensor in methods a) single image depth estimation, b) darkness contour detection, c) Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) regression and 2D Lidar sensor in method d) range geometry. For the works a)-c) the dark scene in the middle of the tunnel is considered as open space and is processed and converted to yaw rate command, while d) examines the geometry of the range measurements to calculate the yaw rate command. Experimental results from real underground tunnel demonstrate the performance of the methods in the field, while setting the ground for further developments in the aerial robotics community.
@article{kanellakis2020look, title = {Where to look: a collection of methods for MAV heading correction in underground tunnels}, author = {Kanellakis, Christoforos and Mansouri, Sina Sharif and Casta{\~n}o Arranz, Miguel and Karvelis, Petros and Kominiak, Dariusz and Nikolakopoulos, George}, journal = {IET Image Processing}, volume = {14}, number = {10}, pages = {2020--2027}, year = {2020}, publisher = {The Institution of Engineering and Technology} }
-
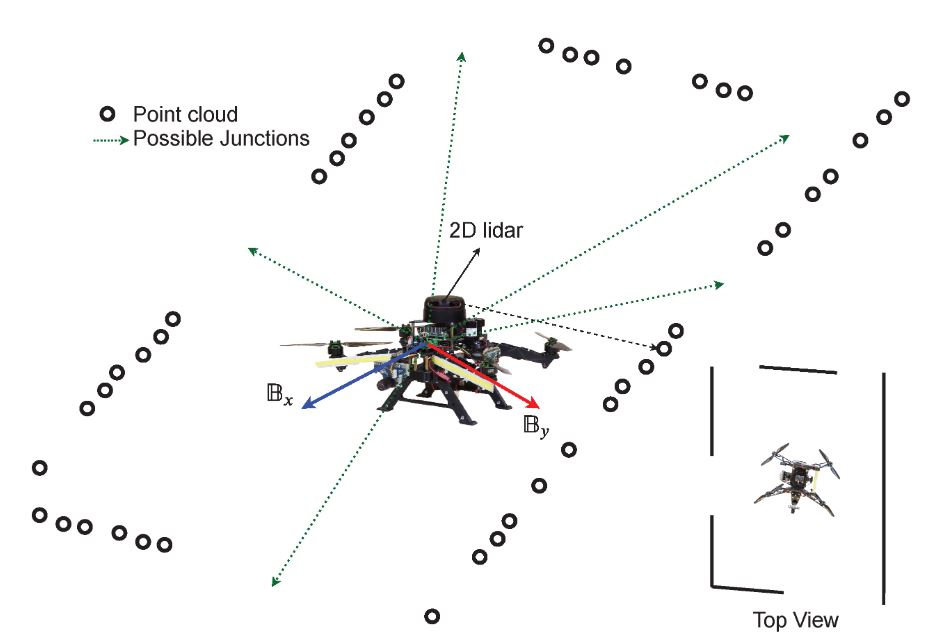 Unsupervised Learning for Subterranean Junction Recognition Based on 2D Point CloudIn 2020 28th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED) 2020
Unsupervised Learning for Subterranean Junction Recognition Based on 2D Point CloudIn 2020 28th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED) 2020This article proposes a novel unsupervised learn- ing framework for detecting the number of tunnel junctions in subterranean environments based on acquired 2D point clouds. The implementation of the framework provides valuable information for high level mission planners to navigate an aerial platform in unknown areas or robot homing missions. The framework utilizes spectral clustering, which is capable of uncovering hidden structures from connected data points lying on non-linear manifolds. The spectral clustering algorithm computes a spectral embedding of the original 2D point cloud by utilizing the eigen decomposition of a matrix that is derived from the pairwise similarities of these points. We validate the developed framework using multiple data-sets, collected from multiple realistic simulations, as well as from real flights in underground environments, demonstrating the performance and merits of the proposed methodology.
@inproceedings{mansouri2020unsupervised, title = {Unsupervised Learning for Subterranean Junction Recognition Based on 2D Point Cloud}, author = {Mansouri, Sina Sharif and Pourkamali Anaraki, Farhad and Castaño Arranz, Miguel and Agha-Mohammadi, Ali-Akbar and Burdick, Joel and Nikolakopoulos, George}, booktitle = {2020 28th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED)}, pages = {802--807}, year = {2020}, organization = {IEEE}, }
